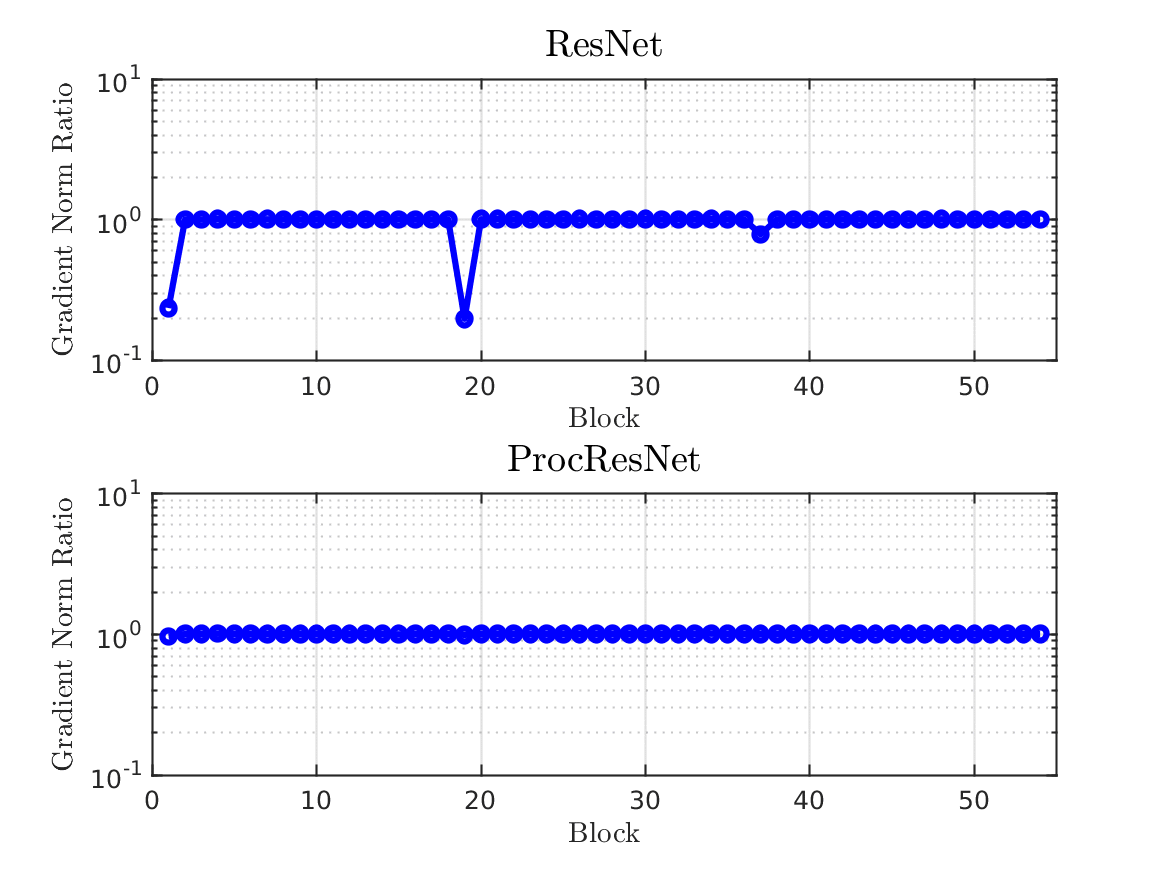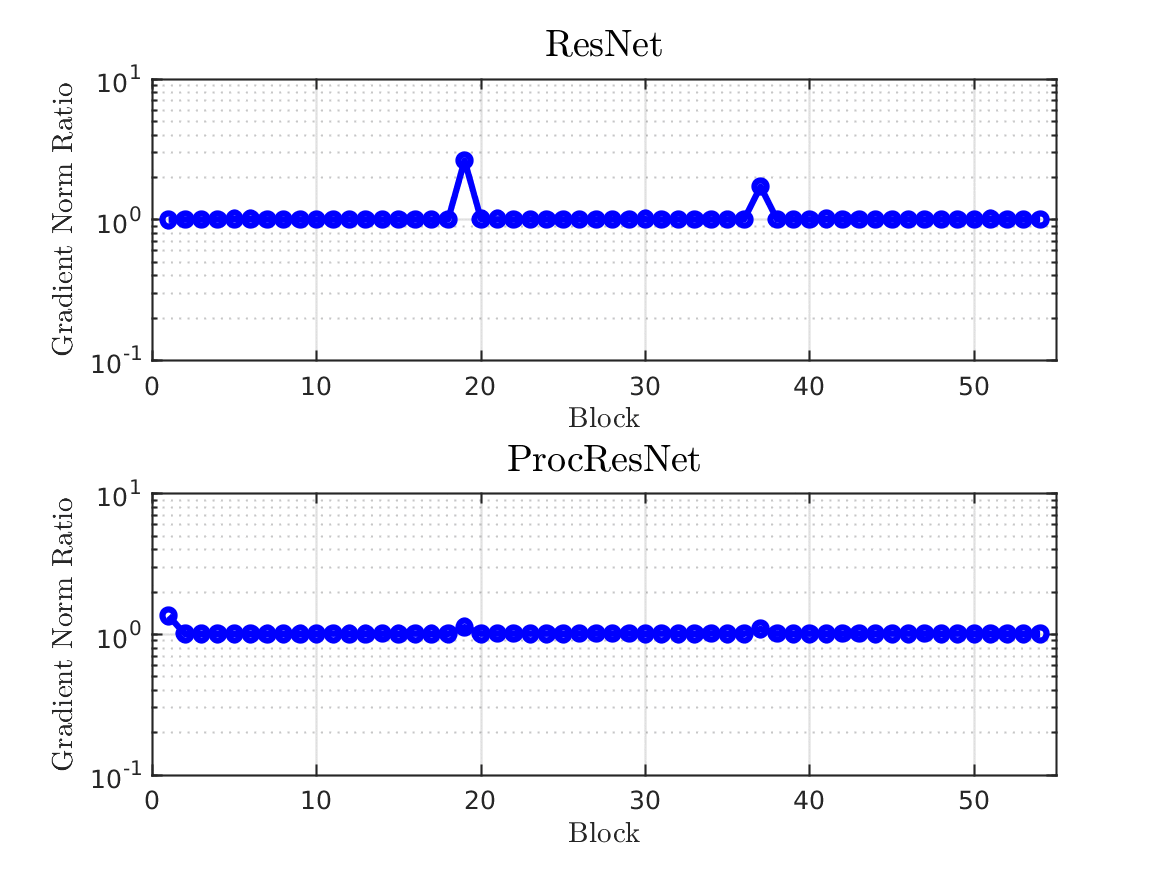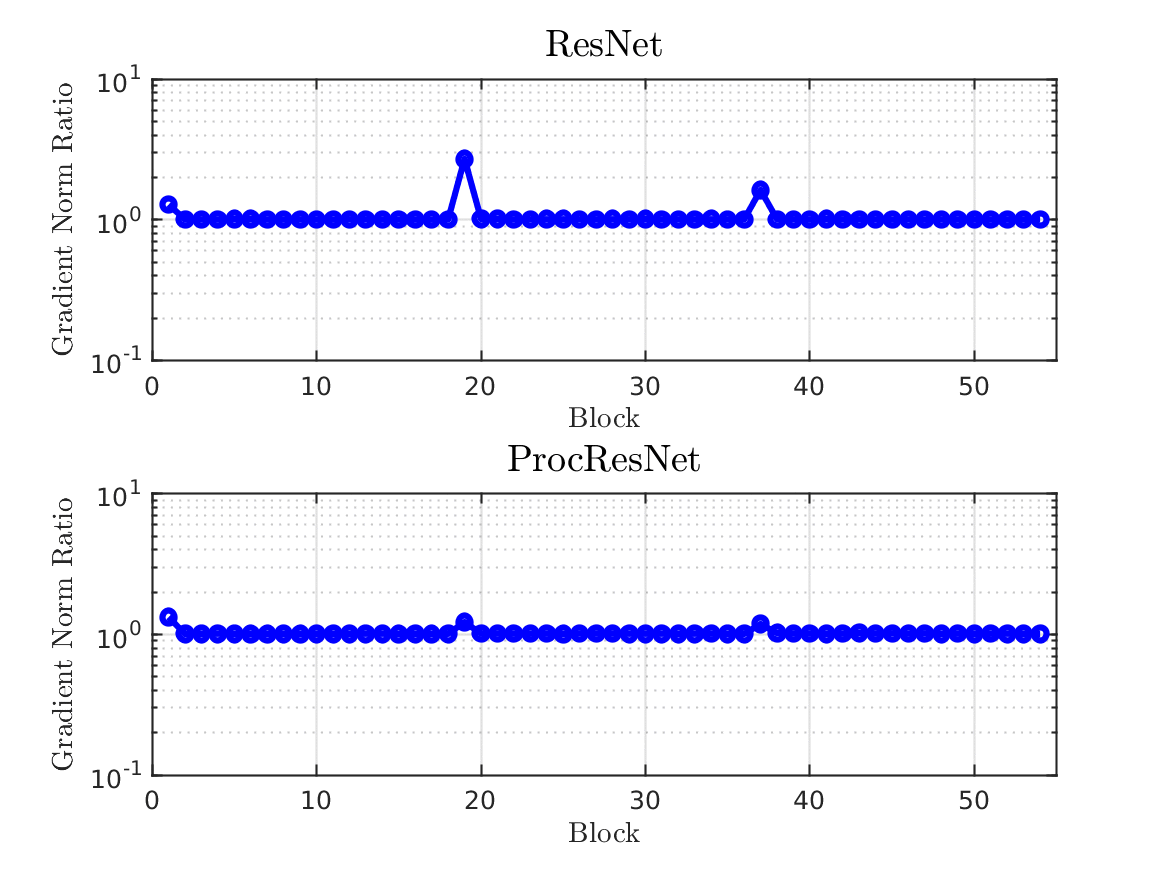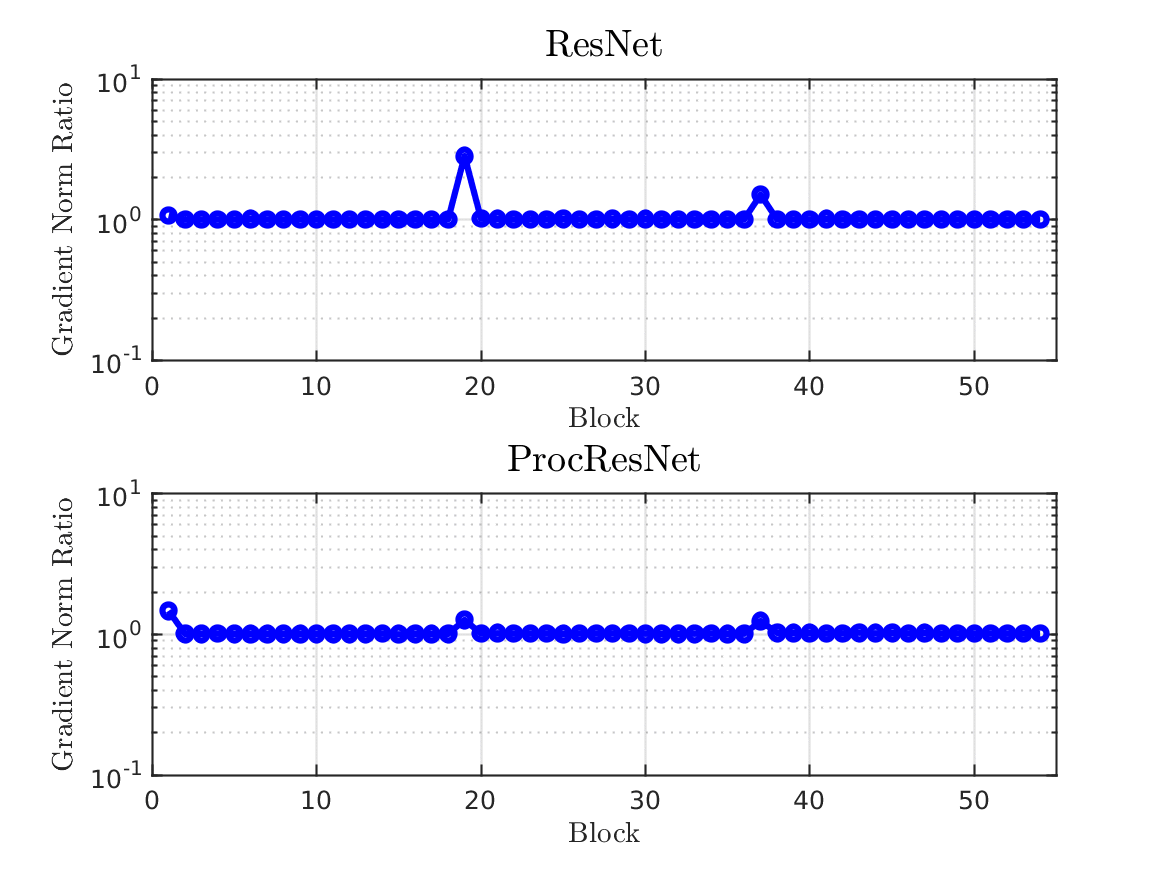
Design and Analysis of Modern Error-Control Coding Schemes
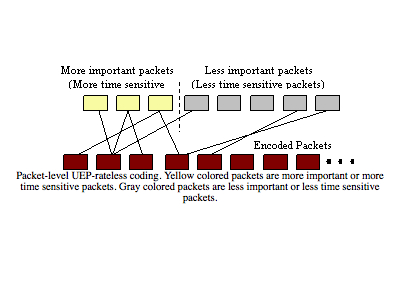
Rateless codes are a new class of codes that have been invented recently. Rateless codes on lossy channels do not assume any knowledge about the channel, unlike the traditional codes. This feature makes them very interesting in the applications that the channel loss is unknown, time-varying, or nonuniform. In the original work on rateless codes, equal error protection (EEP) of all data was considered. EEP would be sufficient in the applications such as multicasting bulk data. However, in several applications, a portion of data may need more protection than the rest of data. For example, in an MPEG stream, I-frames need more protection that P-frames.
In some other applications, a portion of data may need to be recovered prior to the other parts. An example would be on-demand media streaming, in which the stream should be reconstructed in sequence. Such applications raise a need for having codes with unequal error protection (UEP) or unequal recovery time (URT) property. We developed , for the first time, rateless codes that can provide UEP and URT. We analyzed the proposed codes under both iterative decoding and maximum-likelihood decoding. Results are very promising and show the applicability of UEP-rateless codes in many important applications, such as transferring data frames or video/audio-on-demand streaming.
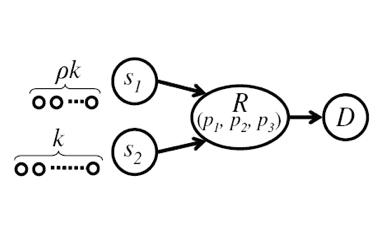
When multiple sources of data need to transmit their rateless coded symbols through a single relay to a common destination, a distributed rateless code can be employed to encode the source symbols instead of several separated conventional rateless codes to increase the transmission efficiency and flexibility. In our research, we have proposed DU-rateless codes, which are distributed rateless codes that can provide UEP for sources with different data lengths. We have designed degree distributions for DU-rateless codes using genetic-algorithms.
We have also designed several rateless codes similar to LT codes with optimum intermediate recovery rate.
Related Publications: UEP and UEP Rateless Coding